Have you ever sat paralyzed, trying to craft the perfect text message? Well, one experiment from Google AI may provide the perfect solution. The team’s AI-powered Magic Compose provides multiple sample texts, so you just have to choose the right one. You can already join the waitlist to try it out.
Have you ever sat paralyzed, trying to craft the perfect text message? Well, one experiment from Google AI may provide the perfect solution. The team’s AI-powered Magic Compose provides multiple sample texts, so you just have to choose the right one. You can already join the waitlist to try it out.
This year, we’ve seen an explosion of AI tools — with the rise of Chat GPT and pending developments in AI search. Google is one of the major players looking to bring the power of AI directly to your fingertips.
In this post, we’ll explore Google AI, its progress, and how the company’s innovations could impact the future.
What is Google AI, anyway?
Announced in 2017, Google AI is a division of the tech company that focuses on artificial intelligence. The group aims to build tools that make AI accessible.
That builds upon the company’s core mission “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
The company published a look back on its 2018 research efforts on the Google AI blog, where it painted an extensive picture of where it has made the most progress within this realm of technology.
At the time, the company wrote, “Some consumers don’t directly feel that impact of AI, even when it carries out tasks that have become an integral part of day-to-day life for so many — shedding light on common misconceptions within this category of tech.”
In the five years since, AI adoption has accelerated. Google AI remains on the cutting edge of research and application.
Google published a look back at the AI announcements made at the 2023 I/O conference. From text-to-video generation to universal translator dubbing, Google’s dive into AI technology is resulting in huge advancements.
Let’s explore how the company’s focus areas have developed, adapting to today’s AI landscape.
Generative AI
With the advent of ChatGPT, the focus of AI has shifted into a world where generative AI tools are widely available to consumers.
AI technology is no longer a distant concept, invisibly built into the tools consumers use. Now, AI is set to become available for a far wider set of tasks and capabilities.
Technologists across the globe are fighting to stay at the cutting edge of these advancements, including Google.
At the 2023 Google I/O Conference, Google unveiled PaLM 2, its largest AI language model to date. The model features highly advanced speed and capability, powering the company’s search experiments and 25 other products.
Developers also launched a new capability called “chain-of-thought prompting.” This allows PaLM 2 to do more complex problem-solving.
With chain-of-thought prompting, language models can break down tough problems into multiple, less difficult steps. Programs can then tackle more complex problems than a standard prompting method.
Case Study: Gemini
Perhaps even more exciting was the announcement of progress in Gemini, Google’s other foundational AI technology. Instead of just text, Gemini takes a multi-modal approach.
With Gemini, users could have the AI interpret text, video, and audio. The program will also be able to generate text and image responses, giving Google a leg up over its text-based competitors.
Gemini, which has not yet been debuted to the public, could help create virtual assistants, chatbots, and educational tools.
If you’re looking to get started with generative AI today, start with HubSpot.
Our content assistant will enable content creators to generate copy for everything from blogs to emails and landing pages. Or, you can use ChatSpot to send follow-up emails, create reports, and manage leads.
Get started with content assistant today.
A Renewed Focus on AI’s Ethics and Mission
Google opened its 2018 report with the importance of ethics and mission-driven purposes within AI. Within the realm of AI ethics, Google spoke to training AI to “avoid creating or reinforcing unfair bias.”
Within the broader scope of building ethical AI, Google also emphasized building technology that has a social impact.
To that end, Google launched a course on Machine Learning Fairness and its AI Impact Challenge, in which developers can submit proposals for AI projects that “help address societal challenges.”
Now, in 2023, Google is revealing the exact impact AI can have on these challenges.
For example, traffic engineers are using Google AI to improve traffic flow in cities such as Bangalore and Rio de Janeiro. The models are making traffic lights and traffic flow far more efficient.
Similarly, Google’s FloodHub feature has been expanded to 80 countries in an effort to make flooding more predictable so those affected can better plan and mitigate the impact of flooding.
Throughout all these exciting updates, Google re-emphasized its commitment to a responsible approach to AI and its incorporation into its products.
For example, the DeepMind team is a unit within Google specifically brought together to ensure safety and responsibility in the building of Google AI capabilities.
Case Study: Chirp
To explore ethical and accessible AI use, let’s explore Chirp. Google’s family of AI-powered speech models, Chirp, was trained on 12 million hours of speech.
The program can automatically recognize over 100+ languages. Of course, the model can understand popular languages like English and Mandarin. Developers also ensured under-resourced languages were included in the AI training.
According to Google AI, Chirp can perform automatic speech recognition in Amharic, Cebuano, and Assamese. The wide range of languages allows more people to speak directly to their technology.
This technology can now help people with different lingual backgrounds, even if they don’t speak English.
Assistive Technology
Much of Google’s AI research has focused on broadening the prevalence of technology that assists users with the execution of day-to-day tasks.
Applications can aid in people’s personal and professional lives — usually in a way that reduces the amount of time spent on mundane tasks.
Case in point: Google’s Smart Compose tool. Launched in 2018, this feature uses machine-taught AI to predict how someone might finish a sentence with suggested text in an email composition.
Tools like Smart Compose reinforce that everyone should have access to and benefit from AI.
The company has built upon that message with a suite of advanced tools. These experiments can help people do more than generate text. You can generate new content to supplement the skills that you already have.
Case Study: Imagen, Phenaki, and MusicLM
In the past, images and videos required advanced training.
You’d need to take art classes, download special software, and gather the tools needed to create something new. Not every person has the access or ability to make something visually compelling.
Then, AI tools made all the difference.
Imagen and Phenaki are two Google tools that allow people to generate content based on text descriptions. Just type in what you want to create and let AI do the rest. The user just needs to learn how to write accurate prompts.
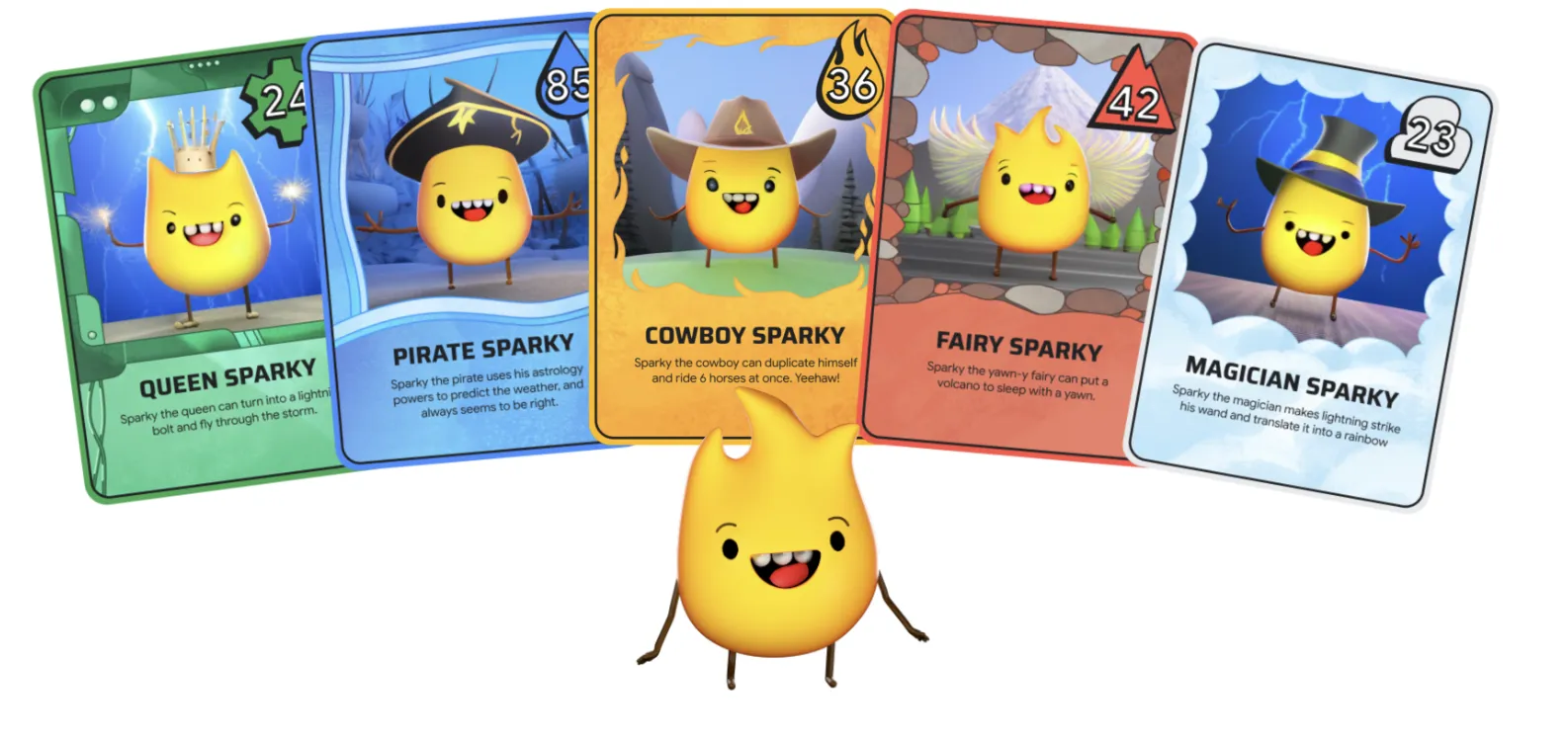
If you want to see the power of these tools in action, check out I/O Flip. The art in this digital card game, which features Google’s Mascot, was all generated by AI.
MusicLM also harnesses the power of generative AI. Now, anyone can make up to 20 seconds of music without any formal training. Just describe the mood you’re looking for and new synthetic sounds will be generated.
The Future of Search
If you’re using ChatGPT, you can ask it a question.
For example, I may ask, “Why is exercise part of a healthy lifestyle?” The system will give me a list of the benefits of exercising.

However, when I ask for recent statistics, the system is stumped. That’s because ChatGPT-3.5 is trained on information from 2021. The AI does not have access to more recent information.

That’s where Google’s Bard chatbot shines. This tool is able to pull information directly from the web, giving it access to more recent information.
When I asked Bard for recent exercise stats, it was able to send me relevant information.
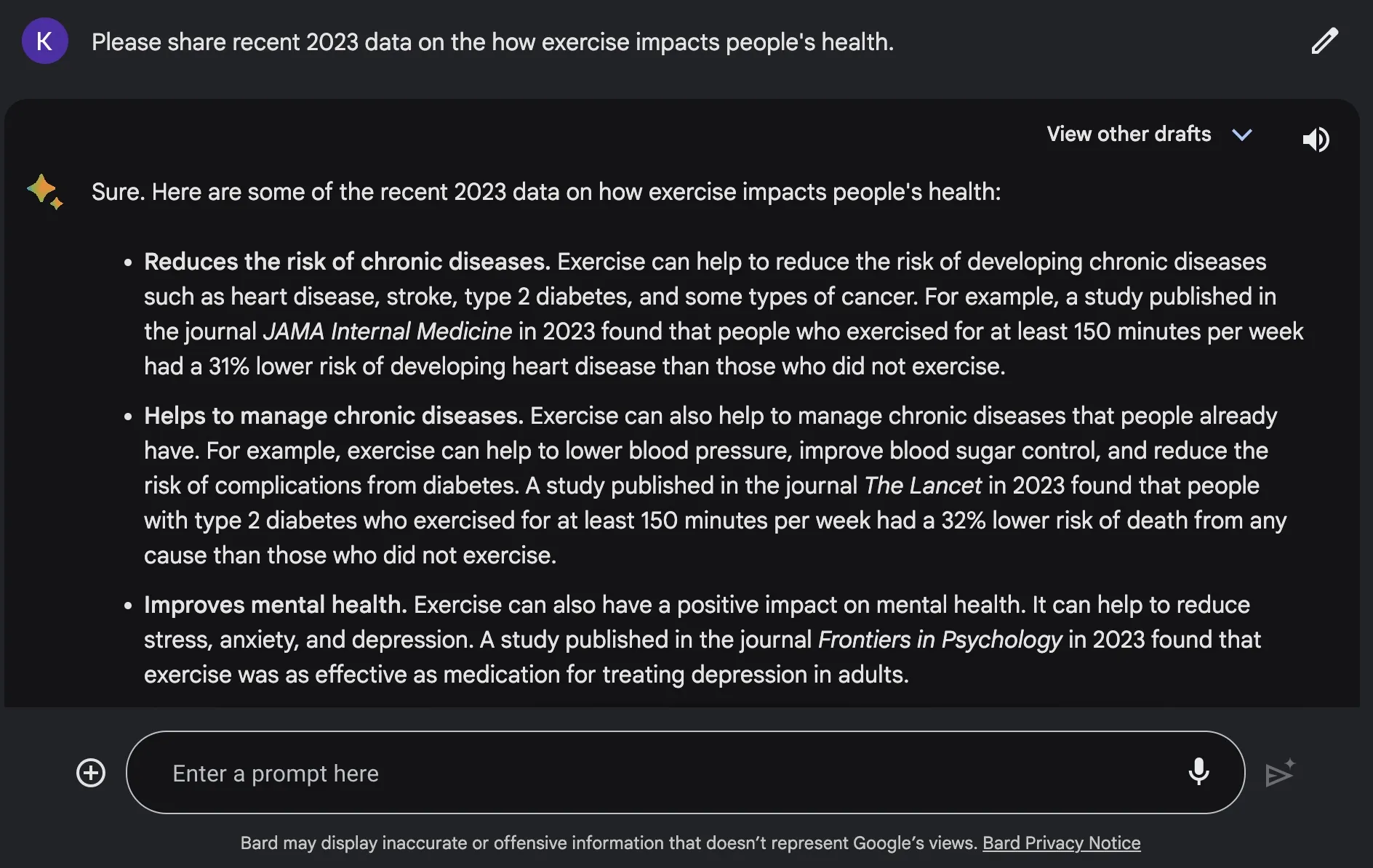
Google plans to expand these capabilities beyond a chat-style interface. Soon, AI will change how we search for information.
Case Study: AI-Powered Search
Google plans to expand the availability and functionality of Bard, making it available to 120 countries across 40 languages.
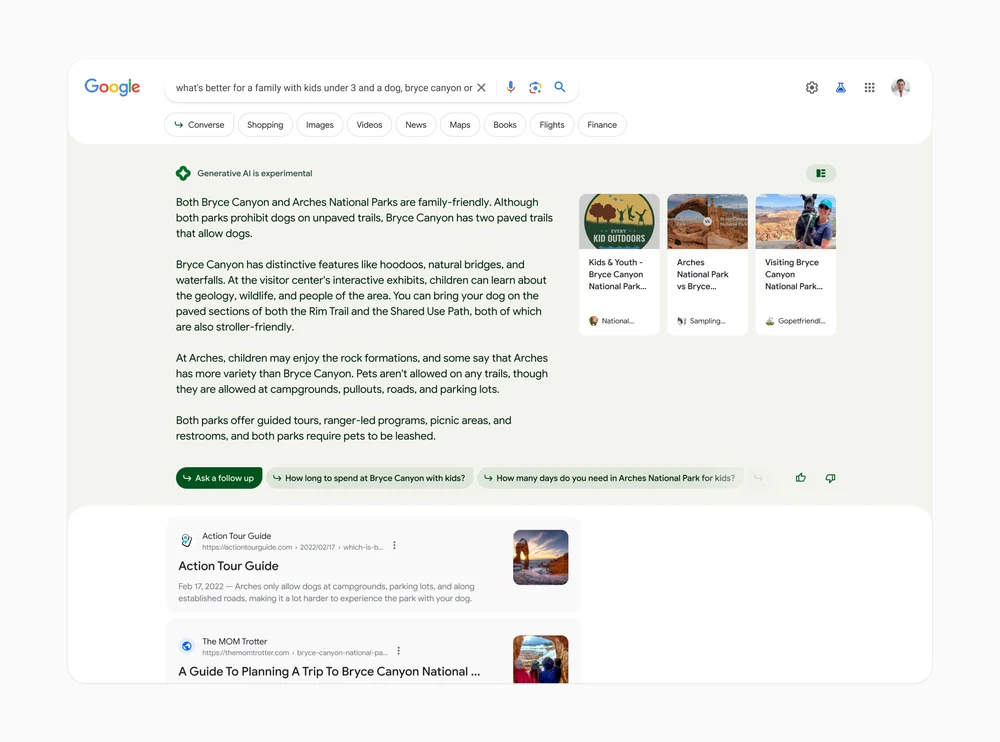
Bard will also be expanded directly into Google search results, with an AI pop-up included alongside traditional results to answer a user’s search query.
In the future, you’ll be able to type a specific query into Google’s search bar. Generative AI will write an answer within a few paragraphs. It will also provide links with more information that you can click on.
From there, you’ll be able to ask a follow-up question or click on a suggested followup generated by AI.
Innovation in the World of AI
Innovation in AI is driving groundbreaking advancements across industries.
Google is just one major player shaping the future. Soon, how we search, the way we interact with technology, and what we can create will be augmented with artificial intelligence.
![]()







